Is Cargo Fire Suppression Enough to Keep You Safe?
Fire Safety in Aviation and Maritime Shipping
In the realm of modern logistics, the secure transportation of goods across skies and seas is paramount for global trade. Yet, in the midst of this complex network of transportation, the looming threat of cargo fires remains a persistent worry. The potential devastation brought by a cargo fire necessitates comprehensive safety measures spanning diverse transit modes.
Both aviation and maritime industries acknowledge the significance of shielding cargo from multifaceted fire risks. Regardless of the mode of transportation, the core objective remains unwavering: preventing and mitigating fire incidents to protect cargo, crew, passengers, and vessels alike.
Amid these challenges, cargo fire suppression systems emerge as crucial safeguards. Tailored for swift detection and containment, they play pivotal roles in curbing fire hazards. However, a holistic safety strategy extends beyond suppression. Early fire detection systems emerge as vital partners, preemptively identifying potential fire threats long before they escalate.
In this article, we unravel the diverse causes of cargo fires, examine the limitations of fire suppression systems, and introduce early detection technologies. Furthermore, we explore the advantages offered by early fire detection systems, highlighting their transformative potential in enhancing cargo safety during transit.
Understanding the Origins and Triggers of Cargo Fires
Cargo fires represent a challenge in both aviation and maritime transportation, posing risks not only to the valuable goods being transported but also to the safety of passengers, crew, and vessels. To effectively address this threat, it’s essential to comprehend the underlying causes of cargo fires and the conditions that can lead to their ignition.
Variety of Ignition Sources
Cargo fires can originate from a diverse array of ignition sources. In the aviation industry, electrical malfunctions, particularly those involving batteries, constitute a significant proportion of fire incidents. The proliferation of lithium-ion batteries, widely used to power various devices, poses a heightened risk due to their potential for thermal runaway—a self-perpetuating chain reaction of overheating that can lead to ignition. Similarly, in the maritime domain, electrical faults, machinery failures, and even hazardous cargo interactions can trigger fires.
Combustible Cargo Contents
Another crucial factor contributing to cargo fires is the nature of the transported goods themselves. Various cargoes, including flammable liquids, gases, chemicals, and even certain types of dry goods, can pose fire risks due to their inherent combustibility or potential for spontaneous ignition. Incorrectly packaged dangerous materials can worsen these risks, highlighting the importance of following safety rules and guidelines.
Cargo Compartment Design and Ventilation
The design of cargo compartments, whether within aircraft or ships, plays a pivotal role in fire propagation. Poor ventilation can allow heat and smoke to accumulate, intensifying the fire and making it more challenging for fire suppression systems to effectively combat the blaze. Similarly, cargo stowage configurations can impact the potential for fires to spread, underscoring the importance of proper loading procedures.
Environmental Conditions
Environmental factors, including temperature and humidity fluctuations, can also contribute to fire risks. Inadequate temperature control can cause temperature-sensitive cargoes to become more prone to ignition. Moreover, the maritime environment introduces the added complexity of saltwater exposure, which can corrode electrical systems and potentially lead to short circuits.
Comprehending the multifaceted nature of cargo fires is crucial for devising effective preventive measures. The confluence of ignition sources, cargo contents, compartment design, and external factors underscores the need for a holistic approach to fire safety that encompasses both prevention and rapid response.
The Limitations of Fire Suppression Systems
Fire suppression systems are important for preventing cargo fires, but they have limitations that need to be recognized. The intricacies of fire dynamics, coupled with the complexities of different cargo compositions and transportation environments, can lead to limitations that require careful consideration. Understanding these limitations is crucial for designing a comprehensive cargo safety strategy that effectively addresses potential challenges.
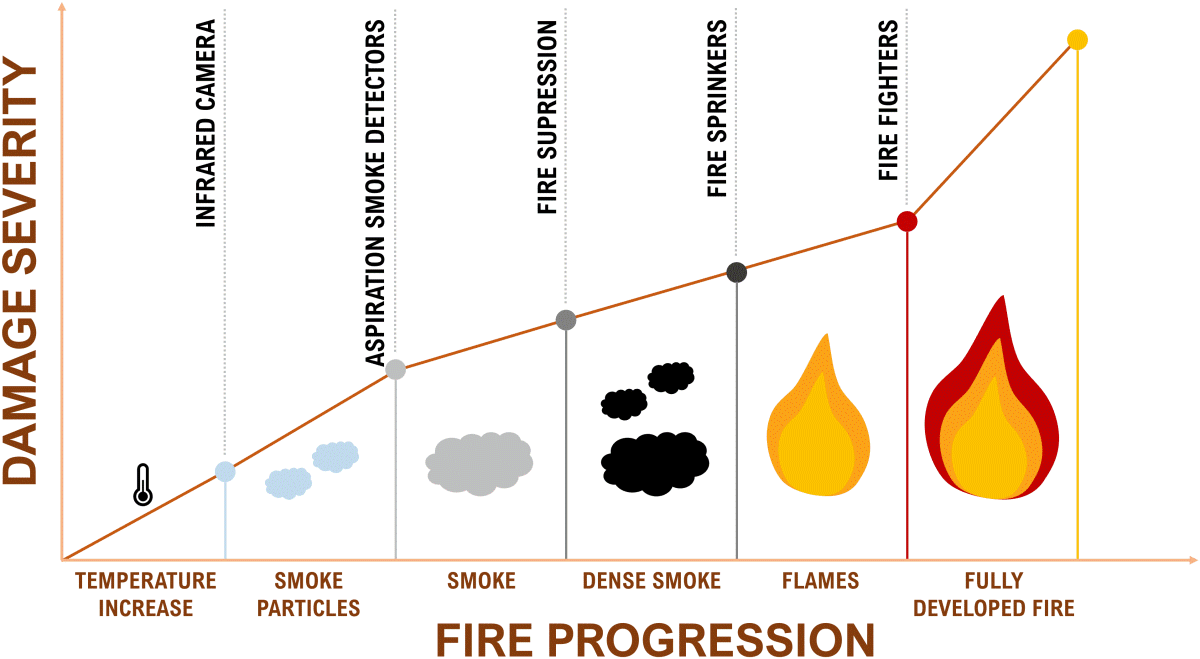
Activation Time and Delay
One of the primary limitations of fire suppression systems lies in the time it takes for the system to activate upon detecting a fire. While these systems are designed for rapid response, even a few seconds of delay can provide a fire with ample opportunity to escalate. Factors such as the location of the fire within the cargo hold, sensor calibration, and activation protocols can impact the system’s effectiveness in containing a blaze before it intensifies.
Potential for Collateral Damage
While suppression agents are invaluable for extinguishing fires, their deployment often carries the risk of collateral damage. For example, the use of foam to smother fires can lead to residue accumulation and potential harm to sensitive cargo items. Striking a balance between swift fire containment and minimizing damage to valuable cargo assets becomes a delicate act that requires careful consideration.
Limited Effectiveness Against Certain Fires
Despite their advancements, fire suppression systems might face challenges when it comes to combating certain types of fires. Fires involving highly reactive chemicals, such as those found in lithium-ion battery packs or industrial materials, can pose formidable obstacles due to their unique ignition mechanisms and the limited efficacy of conventional suppression agents against them.
Incorporating these limitations into the broader understanding of cargo fire safety illuminates the need for a comprehensive approach that combines fire suppression systems with other proactive measures, such as early detection mechanisms and robust safety protocols. By acknowledging and addressing these limitations, aviation and maritime industries can chart a course towards a more secure and reliable transportation of goods across skies and seas.
Enhancing Cargo Safety through Early Fire Detection
Safety doesn’t solely hinge on reactive measures—it also thrives on the foresight to prevent emergencies before they unfold. Early fire detection systems are an important part of defense against fires, working alongside fire suppression systems.
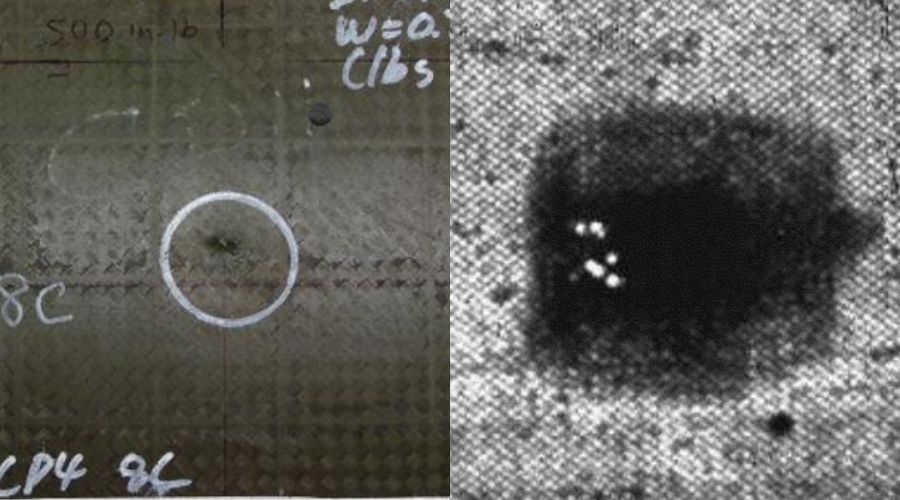
Early fire detection systems serve as vigilant guardians, equipped to identify the first signs of potential fire hazards before they ignite. Among these advanced technologies, infrared cameras stand out as crucial tools in the pursuit of cargo safety.
Infrared (IR) cameras offer a window into the world of heat, revealing otherwise invisible temperature differences. When anomalies in temperature arise, possibly indicating the presence of a fire, these cameras swiftly capture the thermal signatures. Early fire detection systems trigger alarms and alerts when deviations from the norm are detected. Crew members and operators are promptly informed, enabling them to take immediate action, initiate protocols, and potentially avert a full-scale fire event.
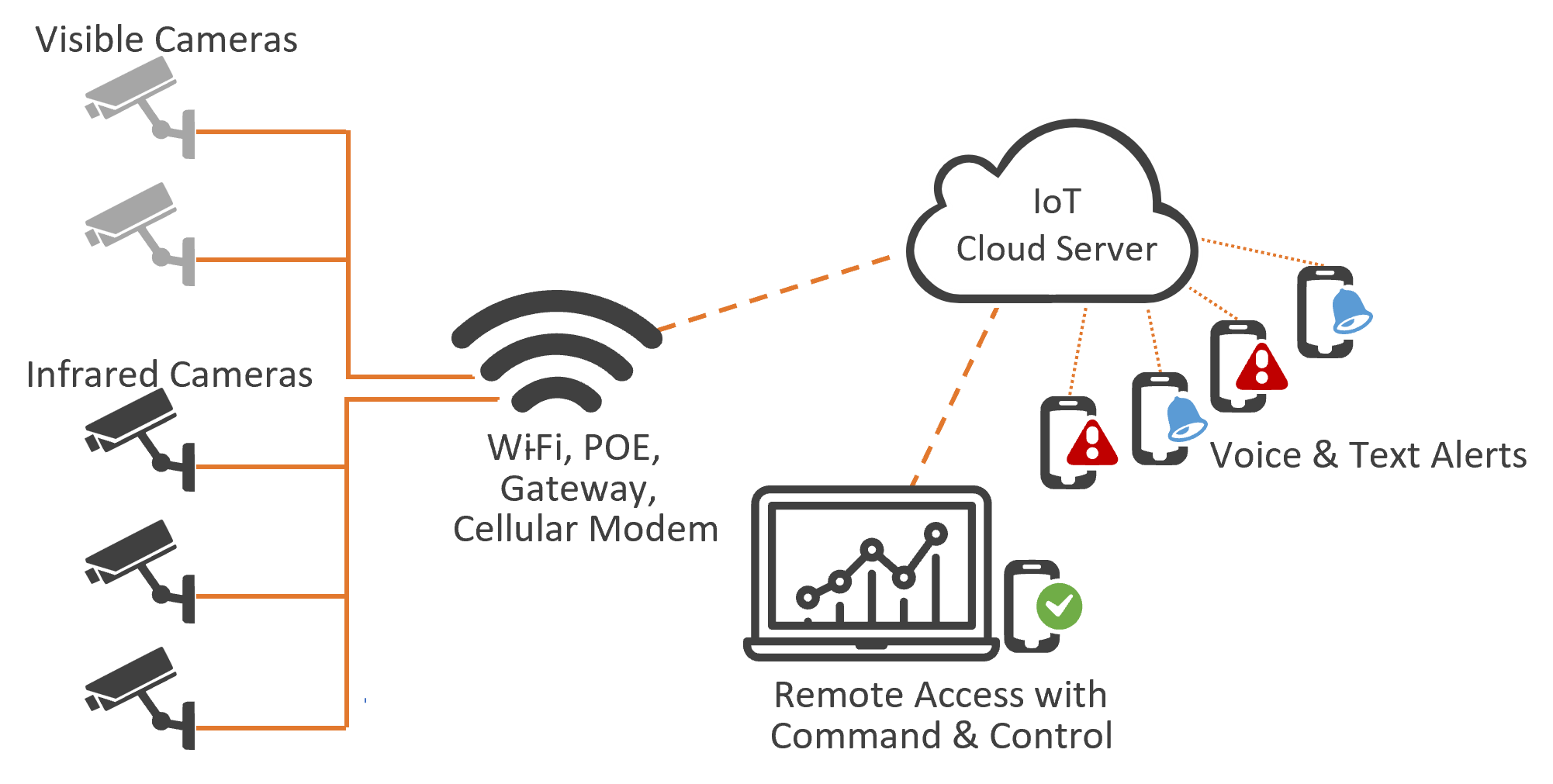
Advantages of Early Detection
The advantages presented by early fire detection systems are both substantial and multifaceted, contributing to a holistic approach to cargo safety:
Proactive Prevention
Early detection systems afford the opportunity to intercept fire risks in their initial stage. By alarming at the earliest indications of trouble, these systems allow operators and crew to intervene before a fire even ignites, thwarting potentially catastrophic events.
Reduced Dependency on Suppression
One of the most compelling aspects of early fire detection is its capacity to curtail the necessity for fire suppression measures. By stopping a fire before it becomes unmanageable, these systems reduce the reliance on aggressive suppression agents, which can sometimes lead to collateral damage or asset loss.
Preservation of Valuables
Early fire detection can be particularly instrumental in safeguarding valuable cargo contents. By preventing fires or detecting them in their initial stages, these systems contribute to the preservation of goods and assets, minimizing financial losses and maintaining the integrity of transported items.
A Symbiotic Approach to Safety
The interplay between fire suppression systems and early detection systems underscores the synergy that underpins modern cargo safety strategies. While fire suppression systems respond swiftly to contained fires, early detection systems extend their protective embrace by stopping potential fires in their tracks. Together, they embody a comprehensive approach that maximizes the potential for a safe and secure journey.
About MoviTHERM:
MoviTHERM – Advanced Thermography solutions was founded in 1999. The company offers solutions for plastic welding, package sealing, and non-destructive testing. In addition, MoviTHERM provides IoT Cloud monitoring solutions for thermal imaging applications for early fire detection, machine condition monitoring, and other applications. MoviTHERM is a Teledyne FLIR Premium Partner and master distributor for FLIR Thermal Cameras for automation and science applications.