Application Examples for Automated Visual Inspection
In an era defined by rapid technological advancements and increasingly demanding consumer expectations, the pursuit of flawless product quality has become a paramount goal for industries worldwide. This pursuit, once reliant on human judgment and painstaking manual inspection, is now propelled by automated visual inspection systems. The fusion of smart cameras, advanced sensors, and sophisticated image processing algorithms has led to a solution that redefines quality control.
Where excellence is no longer a luxury but an expectation, automated visual inspection illuminates the path toward higher standards, greater efficiency, and unshakable consumer trust. In this article, we uncover the inner workings of automated visual inspection, the various camera and sensor types involved, its industry applications, and the clear benefits it offers over manual inspection.
How Automated Visual Inspection Works
Automated visual inspection systems follow a systematic process:
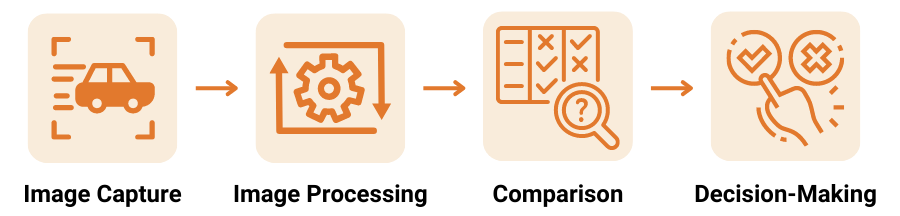
➜ Image Capture
High-resolution cameras capture detailed images of products or components as they move along the production line.
➜ Image Processing
The images are processed using complex algorithms, enabling the system to analyze patterns, shapes, colors, and defects.
➜ Comparison
The processed images are compared to predefined quality standards and specifications.
➜ Decision-Making
Based on the comparison, the system makes real-time decisions on whether the product meets the required standards or needs further inspection or rejection.
Types of Cameras and Sensors in Automated Visual Inspection Systems
Automated Visual Inspection (AVI) systems rely on a diverse range of cameras and sensors, each tailored to specific requirements and industries. The selection of the right type of camera or sensor depends on factors such as the nature of the product, the type of defect to be detected, and the environmental conditions in which the inspection takes place. Listed below are some of the key types of cameras and sensors used in AVI systems.
Infrared Cameras
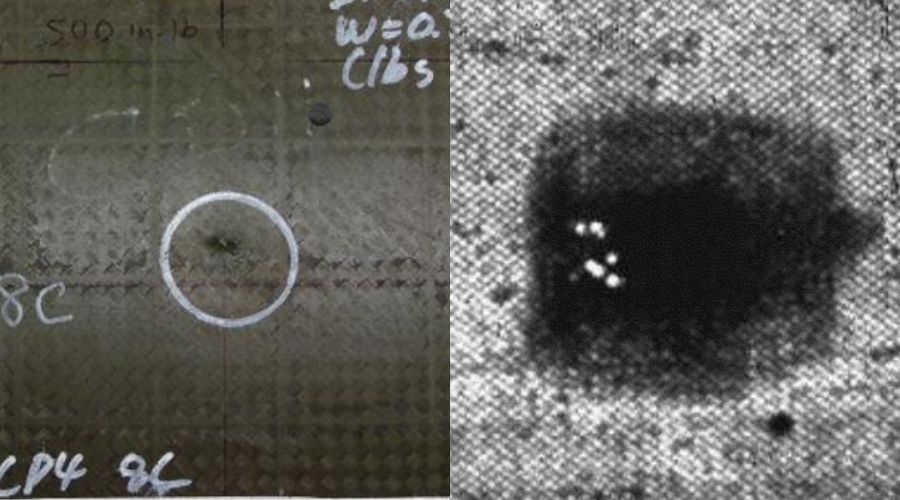
Infrared (IR) cameras, also known as thermal imaging cameras, are invaluable in detecting temperature variations that may indicate defects or malfunctions. These cameras capture the heat emitted by objects, allowing for the identification of hotspots or irregularities that might otherwise go unnoticed.
Applications
Overheating detection, thermal analysis, detection of seal imperfections, irregularities in packaging, and detection of internal defects, cracks, and structural abnormalities.
Industries
Electronics manufacturing (detecting faulty components), Food & beverage industry (detection of seal imperfections, leaks, and irregularities in packaging), and Aerospace (detection of internal defects, cracks, and structural abnormalities in aircraft components).
Color Cameras
Color cameras are used to inspect products based on their visual appearance, such as color variations, patterns, or surface defects. These cameras are vital in industries like textiles, packaging, and cosmetics, where color consistency plays a significant role in product quality.
Applications
Color consistency assessment, pattern recognition, and label verification.
Industries
Textiles (fabric color and pattern matching), Cosmetics (checking color of products), and Food Packaging (label accuracy).
3D Cameras and Depth Sensors
3D cameras and depth sensors create three-dimensional models of objects, enabling the AVI system to analyze not only surface defects but also deviations in shape and dimensions. These sensors are particularly useful in industries where precise measurements are crucial, such as manufacturing and aerospace.
Applications
Dimensional analysis, shape assessment, and contour inspection.
Industries
Aerospace (verification of complex aircraft components), Automotive (measuring car body dimensions), and Consumer electronics (ensuring product casing fits precisely).
Hyperspectral Cameras
Hyperspectral cameras capture images across a wide range of wavelengths, allowing for the identification of materials based on their unique spectral signatures. These cameras are vital in industries like agriculture, where they can detect disease, pest infestations, or variations in crop health.
Applications
Material identification, crop health analysis, and chemical composition assessment.
Industries
Agriculture (identifying diseased plants), Food inspection (checking for spoilage), and Environmental monitoring (detecting pollutants).
Laser Sensors
Laser sensors are used to measure distances, profiles, and dimensions accurately. They are particularly effective in assessing complex shapes and verifying the alignment of components.
Applications
Dimensional measurements, profile analysis, alignment verification.
Industries
Manufacturing (checking part dimensions), Automotive (ensuring proper tire alignment), and Robotics (verifying precise robot arm positioning).
The diversity of cameras and sensors available for automated visual inspection underscores the versatility of this technology. By leveraging the strengths of various sensors, AVI systems can cater to the specific needs of different industries, ensuring accurate, efficient, and comprehensive quality control processes.
Advantages of AVI over Manual Inspection
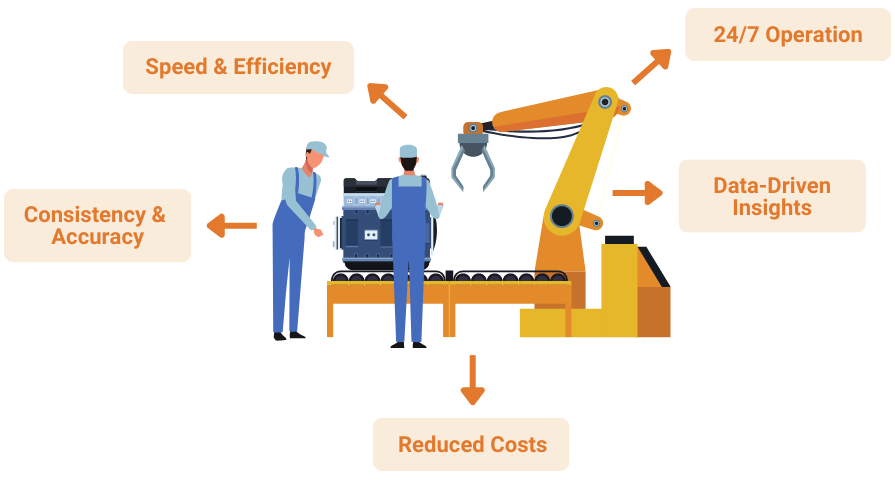
➜ Speed and Efficiency
AVI systems can inspect products at an incredibly high speed, far surpassing the capabilities of manual inspection, leading to faster production cycles.
➜ Consistency and Accuracy
AVI eliminates the variability associated with human judgment, ensuring every product is evaluated against the same standards with unparalleled accuracy.
➜ Reduced Costs
While initial setup costs might be higher, the long-term benefits include reduced waste, fewer recalls, and decreased labor costs due to reduced need for manual inspection.
➜ 24/7 Operation
Automated visual inspection operates around the clock, providing consistent quality control even during non-working hours.
➜ Data-Driven Insights
The data collected from AVI systems can be analyzed to identify trends, patterns, and potential areas for process optimization.
Conclusion
Automated Visual Inspection is a dynamic force reshaping quality control across industries. With its advanced technology, diverse sensors, and real-time insights, AVI empowers businesses to ensure product integrity and exceed consumer expectations. This evolution towards precision, efficiency, and elevated standards signifies not just a transformation in inspection methods, but a reimagining of quality itself.
About MoviTHERM:
MoviTHERM – Advanced Thermography solutions was founded in 1999. The company offers solutions for plastic welding, package sealing, and non-destructive testing. In addition, MoviTHERM provides IoT Cloud monitoring solutions for thermal imaging applications for early fire detection, machine condition monitoring, and other applications. MoviTHERM is a Teledyne FLIR Premium Partner and master distributor for FLIR Thermal Cameras for automation and science applications.













