The Top 9 Different Types of Non Destructive Testing
What is Non-Destructive Testing?
Non-destructive tests (NDT) are methods that do not damage the parts being tested. NDT uses various inspection techniques to assess individual or group components. By employing different principles from physics, chemistry, and mathematics, NDT can test components without causing damage.
NDT can also be referred to as non-destructive evaluation/examination (NDE) or non-destructive inspection (NDI).
Types of Non-Destructive Testing Methods
Below are 9 common types of non-destructive testing being used today:
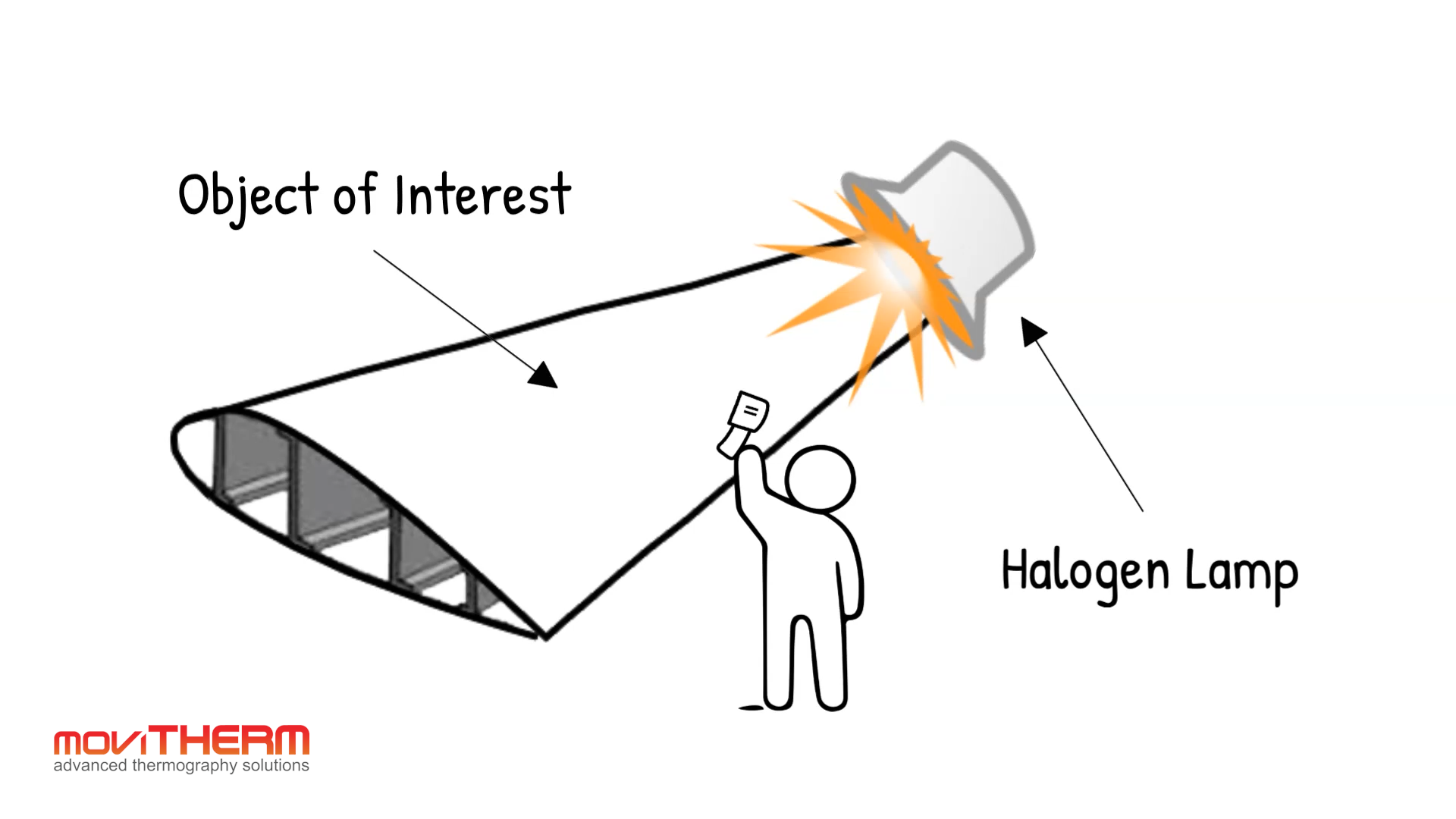
1. Thermal/Infrared Testing
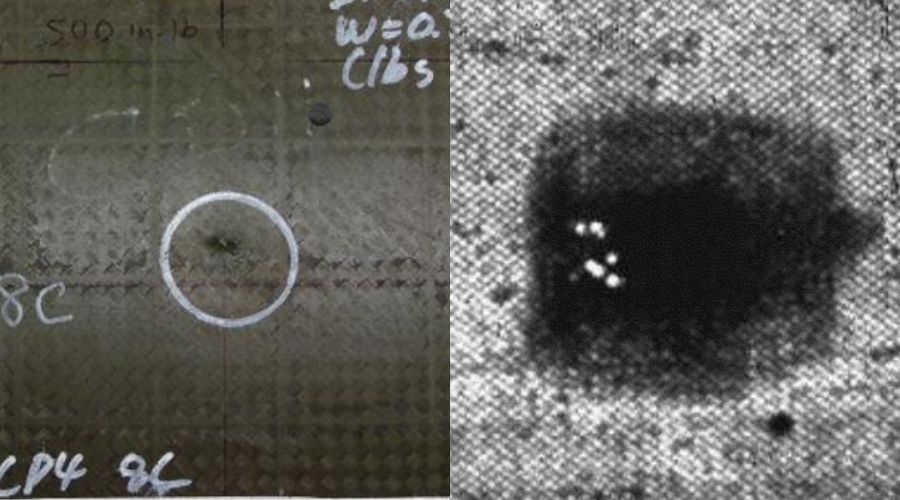
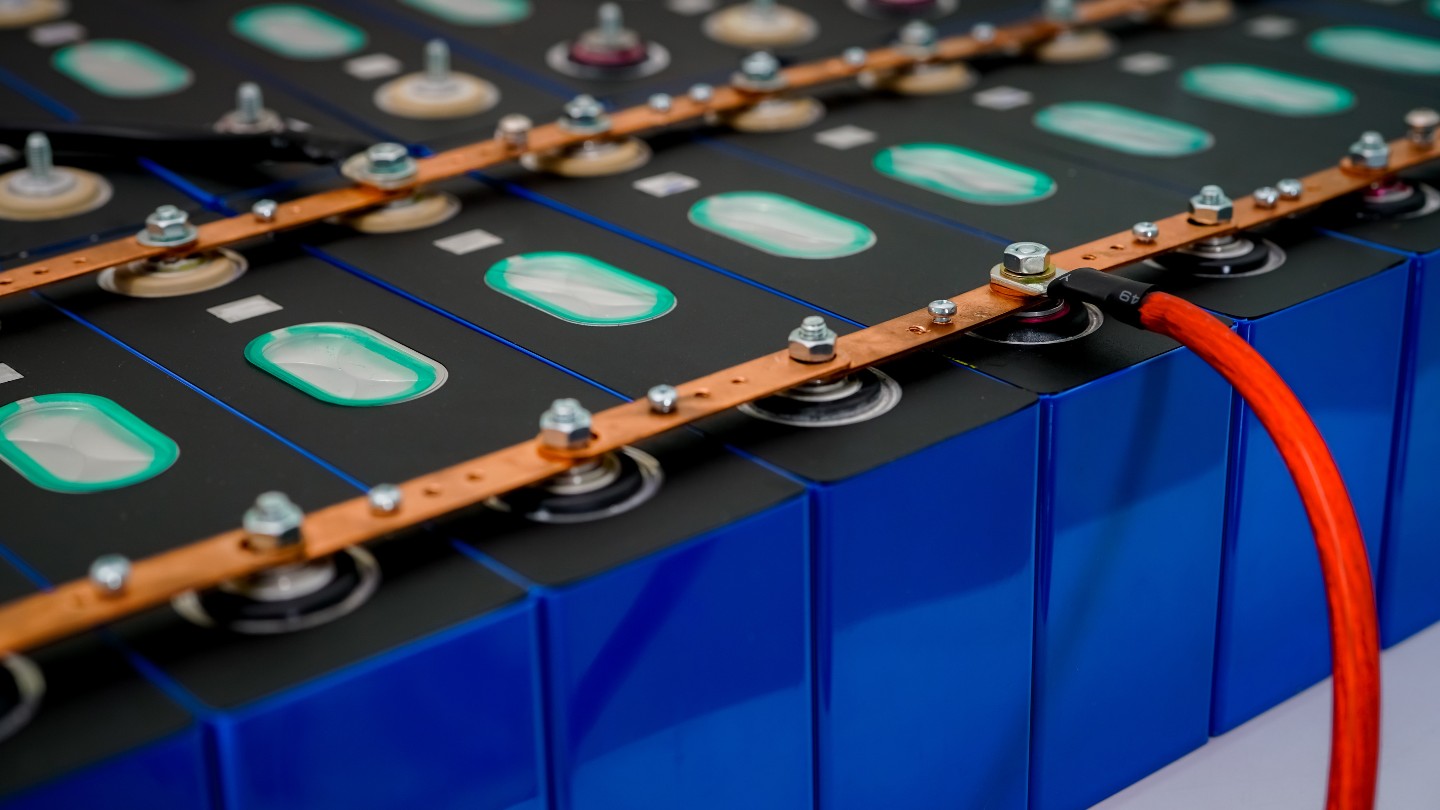
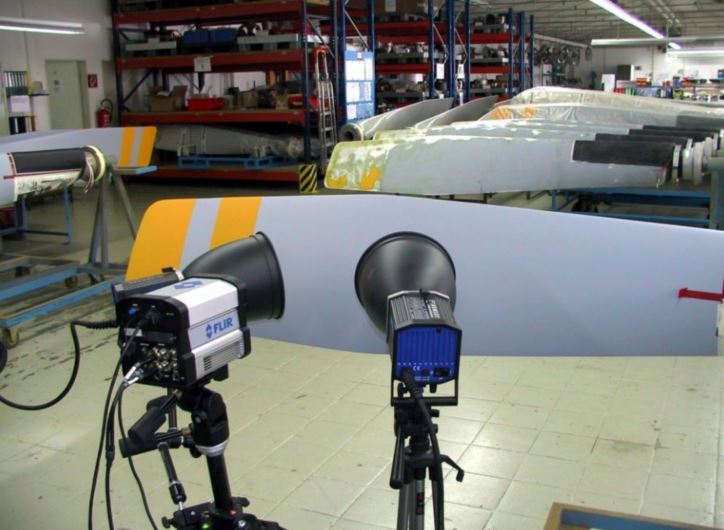
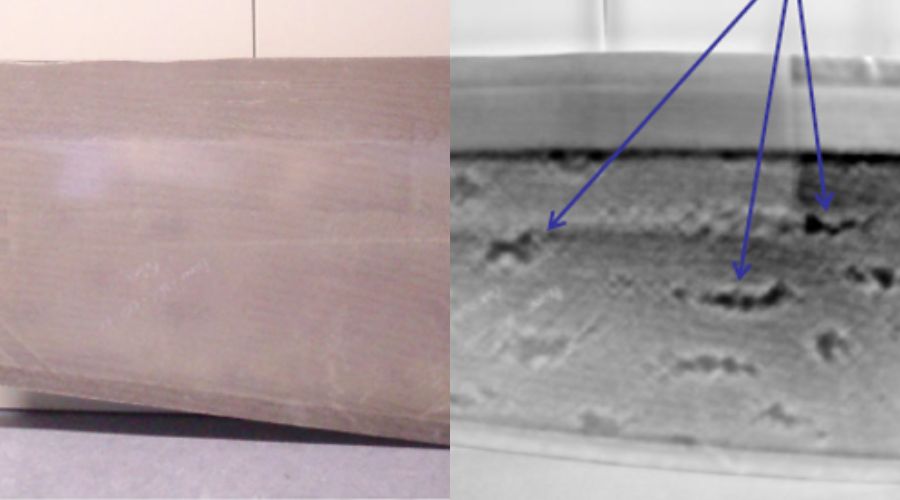
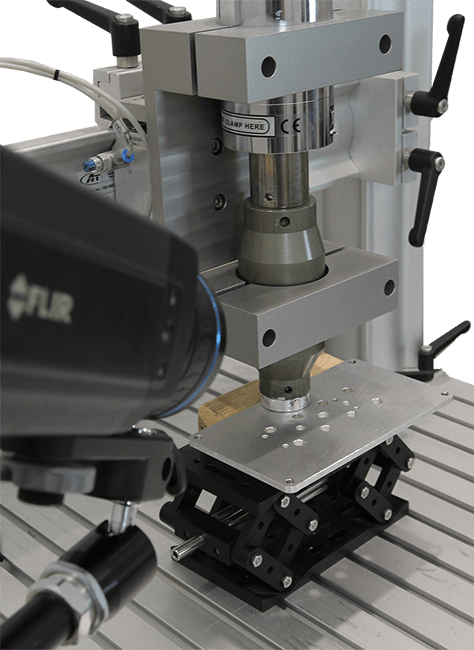
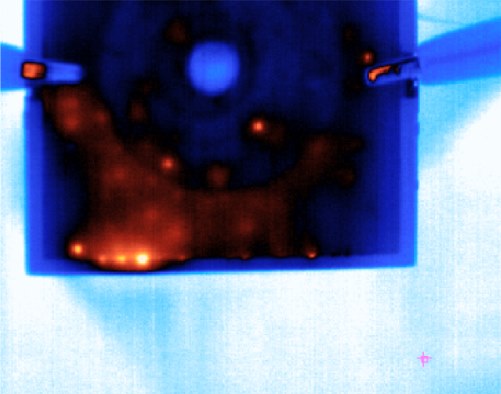
Flash Thermography for Battery Inspection
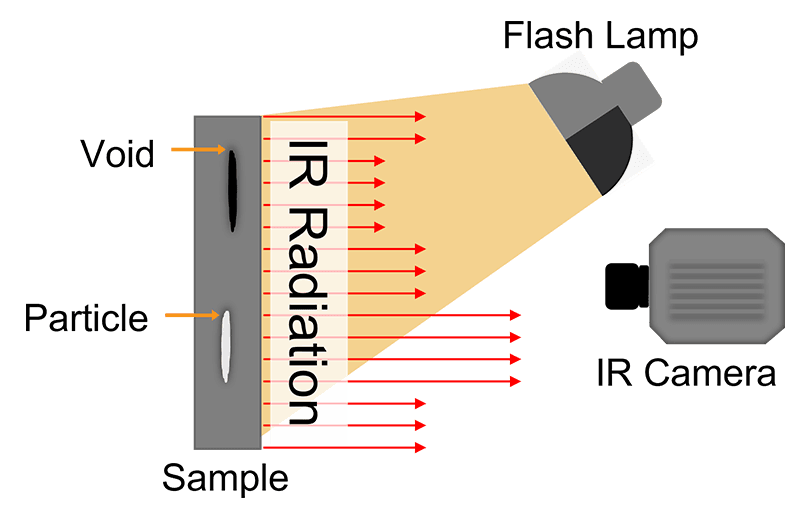
Infrared Non-Destructive Testing has been around for more than 30 years, but has recently gained more momentum. Infrared non-destructive testing is based on the principle of thermal wave imaging. It is considered an active thermography method, as opposed to a passive method.
The active part comes from using an external heat source to warm up the part. Whereas in standard thermography, the camera is usually capturing heat, inherent to the process.
Examples of Thermal/Infrared Inspections:
Finding disbonds in aluminum structures like on an aircraft fuselage or seeing corrosion behind painted surfaces. Other examples include: identifying failure points in microelectronics, evaluating laser weld penetration, and visualizing wheel cracks.
2. Radiography Testing
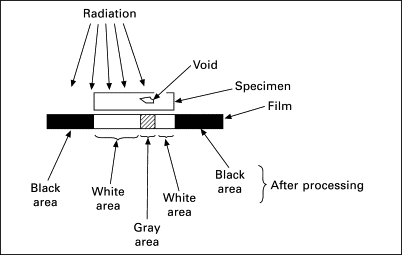
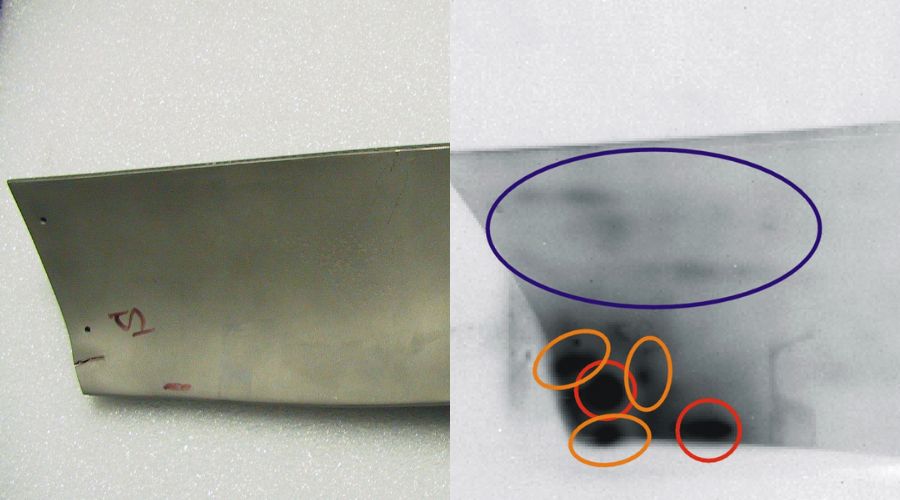
Radiographic Testing (Image Source)
Radiographic testing (RT) uses X-radiation or gamma radiation to find imperfections in a component or system. An X-ray generator or radioactive isotope is used to send radiation into the material being tested. The radiations are then caught by a detector. The resulting shadowgraph is then used by inspectors to look for potential issues.
Example of Radiography Inspections:
X-rays and CT scans can be used in industrial radiography to see detailed images of the tested material.
3. Visual Inspections

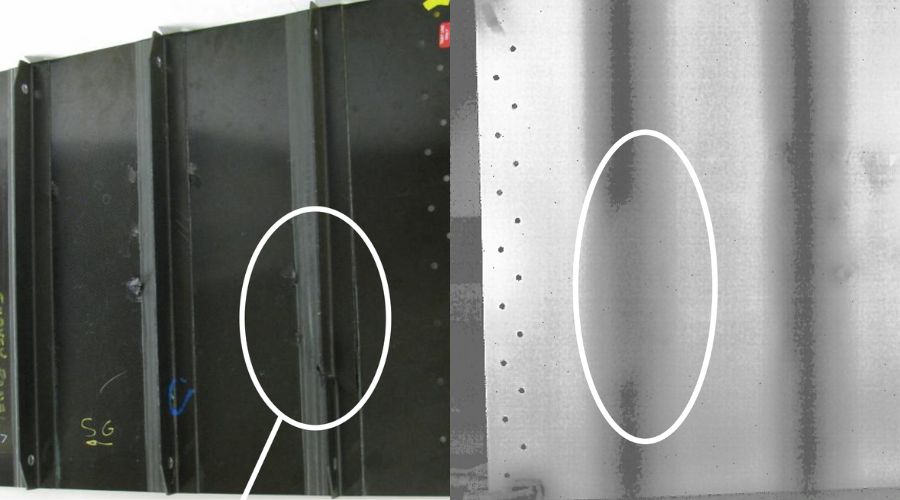
Visual Checks
Visual testing is a way of checking the condition of a material by looking at it. This is the most basic form of testing, and you can do it just by looking at the material. For more detailed visual inspections, you can use a Remote Visual Inspection device to get a closer look.
Example of Visual Testing:
Maintenance professionals use the visual testing method on a daily basis to check for common signs of wear and tear on industrial machinery.
4. Leak Testing
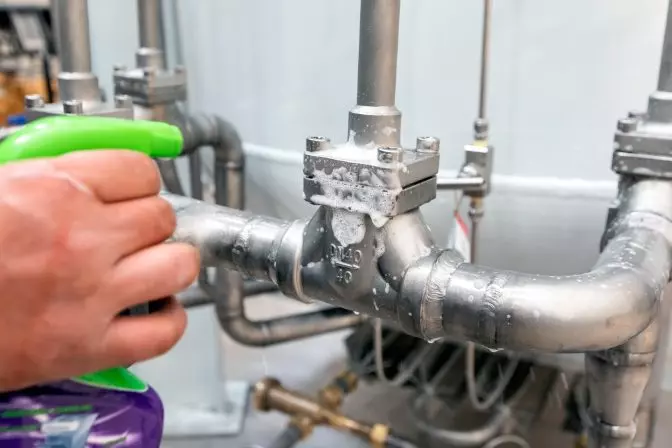

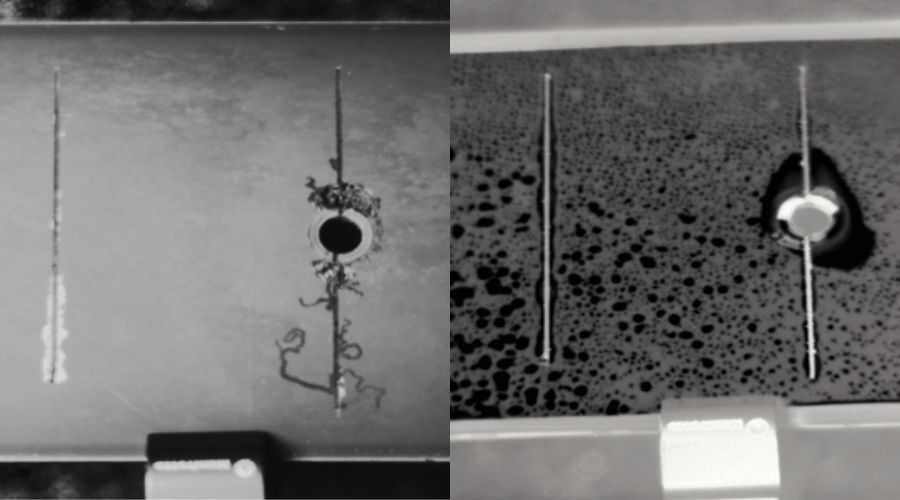
Leak Testing – Bubble Test
Leak testing is used to study leaks and identify defects in structures or vessels. Inspectors often use soap-bubble examinations, pressure gauges, and listening devices to conduct leak testing.
Example of Leak Testing:
A good example of leak testing is using it to find leaks in sealed packaging or devices that do not include an opening for filling.
5. Acoustic Emission Testing
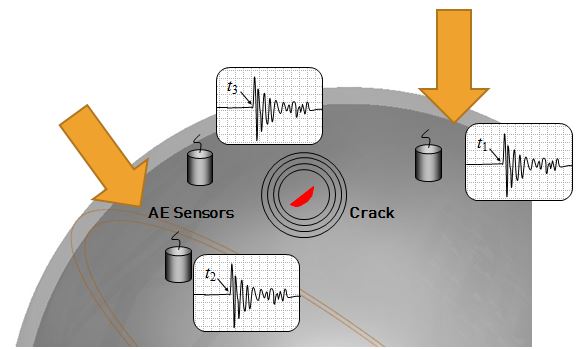
Accoustic Emission Testing (Image Source)
Acoustic emission (AE) testing uses acoustic emissions to identify potential defects in an asset. This testing involves looking for acoustic energy bursts, as these bursts indicate defects. The arrival time, location and intensity of a burst are also examined to identify potential issues.
Example of Acoustic Emission Testing:
AE testing is commonly used to inspect structures such as pressure vessels, pipelines, storage tanks, aircraft structures and steel cables for any defects.
6. Ultrasonic Testing
Ultrasonic Testing
Ultrasonic testing uses high-frequency sound waves to detect and evaluate flaws, measure dimensions, and characterize materials. It is performed with an ultrasonic receiver and transmitter.
Example of Ultrasonic Inspections:
Ultrasonic testing can be used to identify defects and deformation in the wheels and axles of railway carriages.
7. Magnetic Particle Inspection
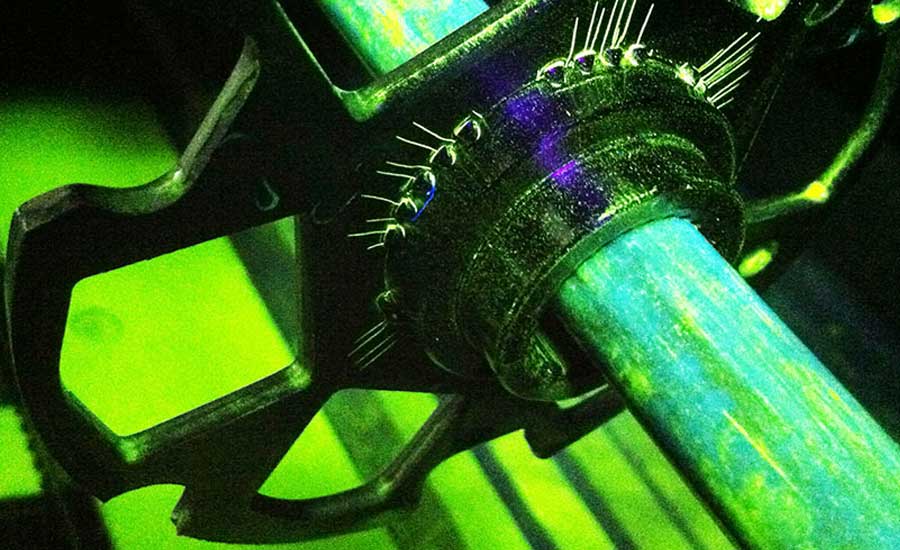

Magnetic Particle Inspection (Image Source)
Magnetic particle testing is a process of detecting flaws in a material by observing disruptions in the flow of the material’s magnetic field. To carry out these tests, an inspector first induces a magnetic field in a magnetically susceptible asset. They then sprinkle iron particles over the surface of the material. These particles will reveal any disruptions, providing a visual indication of where the imperfections are located.
Examples of Magnetic Particle Testing:
A good example of magnetic particle testing is using it to inspect the internal and external surfaces of boiler and pressure vessels.
8. Liquid Penetrant Testing

Liquid Penetrant Testing Example
When conducting liquid penetrant testing, an inspector will apply a coating of liquid with a fluorescent or visible dye to an asset. They will then remove any excess solution from the surface of the asset. The remaining solution is left in any breaks or defects in the surface. These defects will be revealed by the dye, which can then be removed using ultraviolet light. With regular dyes, inspectors will study defects by the contrast between the developer and penetrant.
Example of Liquid Penetrant Inspection:
A good example for penetrant testing can be used for inspecting weld metal build-up on plates.
9. Eddy Current Testing
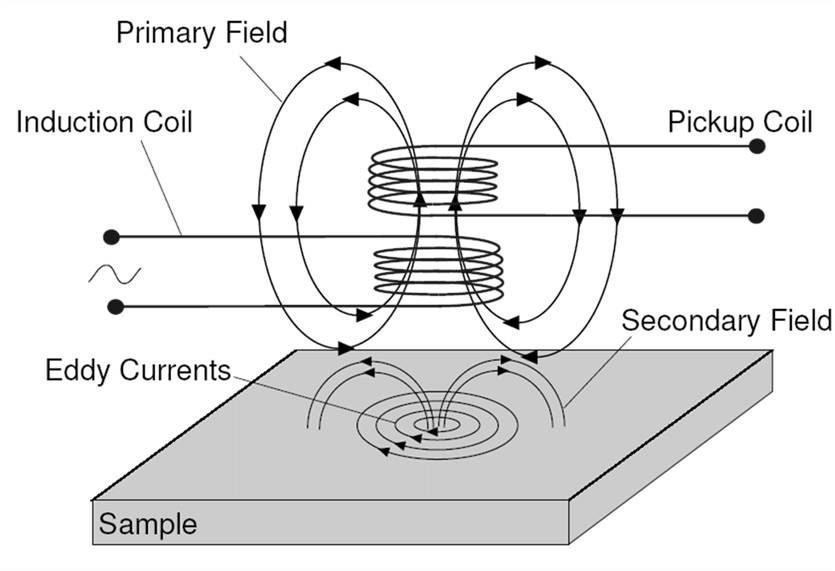
Eddy Current Testing (Image Source)
Eddy current testing is a form of electromagnetic testing where inspectors measure the strength of eddy currents (electrical currents) in a material’s magnetic field. By looking for interruptions in the current, inspectors can often spot defects in the asset or material.
Examples of Eddy Current Testing:
This type of test method can be used for surface scanning, subsurface inspection, weld inspection, fastener hole inspection, tube inspection, heat treatment verification, and metal grade sorting.
What industries use NDT?
Many different industries utilize different types of non-destructive testing to ensure their materials, systems and assets are in good condition and free from defects. For example, companies employing manufacturing and fabrication processes often use NDT to ensure products have the required reliability and integrity. Those in manufacturing also use NDT to keep their products consistent and better control their manufacturing processes.
Non-destructive testing is used for condition assessment and quality control in a wide range of industries, which include (but are not limited to):
- Mining
- Automotive
- Oil and gas
- Medical Devices
- Aerospace
- Maritime
- Military and defense
- Power generation
- Manufacturing
- Packaging
- Waste Management
Turn to MoviTHERM for Infrared Non-Destructive Testing Solutions
MoviTHERM provides infrared NDT solutions to help engineers, researchers, and developers solve problems that cannot be resolved with traditional passive infrared test methods. MoviTHERM’s irNDT solutions use active excitation and intelligent algorithms to tease out the finest internal details of a material.
Find out more about MoviTHERM’s infrared non-destructive testing solutions today. If you have any questions, please feel free to contact us.
About MoviTHERM
MoviTHERM – Advanced Thermography Solutions was founded in 1999. The company offers solutions for plastic welding, package sealing, and non-destructive testing. In addition, MoviTHERM provides IoT Cloud monitoring solutions for thermal imaging applications for early fire detection, machine condition monitoring, and other applications. MoviTHERM is a Teledyne FLIR Premium Partner and master distributor for FLIR Thermal Cameras for automation and science applications.